Beyond Traditional Treatment: Exploring Cutting-Edge Cancer Prevention Methods
Cancer continues to be a leading global health issue, with rising rates of diagnosis and mortality. While traditional treatments like chemotherapy and radiation have significantly improved cancer care, there is a growing need for innovative, more effective strategies. This is especially true for older adults, who face increased cancer risks due to factors like weakened immune systems and prolonged exposure to carcinogens over time. In this article, we will explore cutting-edge methods in cancer prevention that could reshape healthcare, with a focus on how these strategies benefit older populations.
1. Early Detection: The Key to Preventing Cancer
Early detection is a critical component of cancer prevention. The sooner cancer is detected, the better the chances for successful treatment. Recent technological advancements have made early detection more accurate and accessible.
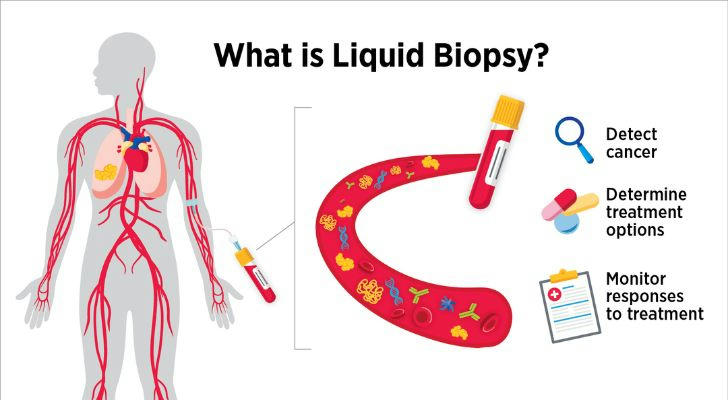
Liquid Biopsy: Liquid biopsy is a groundbreaking method for detecting cancer through a simple blood test. Unlike traditional biopsies, which involve surgery, liquid biopsies are non-invasive and offer faster results. For older adults, this approach is especially beneficial, as it provides an easier option for early cancer detection without the need for invasive procedures. According to a study by the American Cancer Society, liquid biopsy is expected to detect cancer in its earliest stages with up to 90% accuracy, offering hope for early intervention.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) Diagnostics: AI technologies are revolutionizing medical diagnostics. AI algorithms are capable of analyzing medical images with remarkable precision, detecting even the smallest signs of cancer that might be missed by human doctors. A 2020 study from the Journal of the National Cancer Institute found that AI diagnostic systems correctly identified breast cancer in mammograms with 99% accuracy. For older adults, whose access to frequent medical check-ups may be limited, AI-powered diagnostics provide an efficient tool for early cancer detection.
Genetic Testing: Genetic testing is an essential tool in predicting an individual’s risk of developing certain types of cancer. A 2019 study published in JAMA Oncology showed that genetic testing could accurately identify individuals at high risk of developing colorectal cancer, which is one of the most common cancers among older adults. This personalized approach helps healthcare providers create preventive strategies tailored to an individual’s genetic makeup.
2. Strengthening the Immune System: A New Era of Prevention
A robust immune system plays a crucial role in preventing cancer. Enhancing immune function is a promising approach, especially for older adults whose immune systems naturally decline with age.
Cancer Vaccines: Vaccines designed to prevent cancer are making significant progress. For example, the HPV vaccine is already reducing the incidence of cervical cancer, and researchers are working on vaccines for liver and pancreatic cancer. A study published in The Lancet Oncology found that the HPV vaccine can prevent up to 90% of cervical cancers. For seniors, these vaccines offer an opportunity to reduce cancer risk linked to viral infections.
Gut Microbiome Health: The health of our gut microbiome is increasingly recognized for its impact on cancer prevention. A balanced microbiome supports the immune system and reduces inflammation, both of which help lower cancer risks. Research from the National Institutes of Health shows that maintaining a healthy gut can improve immune function and prevent the development of tumors. For older adults, adopting a diet rich in fiber, probiotics, and prebiotics can support a healthier gut microbiome.
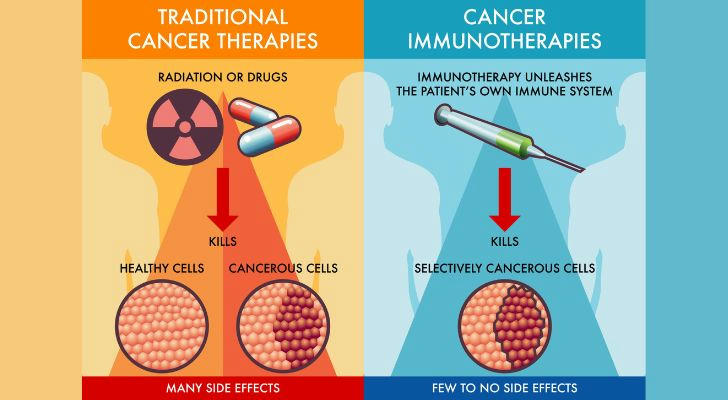
Immunotherapy: Immunotherapy is a revolutionary treatment that enhances the immune system’s ability to recognize and destroy cancer cells. In clinical trials, immunotherapy has shown success in treating cancers that were previously hard to treat, such as melanoma and lung cancer. For seniors, immunotherapy could provide a powerful tool for boosting the immune response and reducing cancer risks.
3. Nutrition and Lifestyle: Foundations of Cancer Prevention
A healthy lifestyle—particularly good nutrition and regular physical activity—is key to cancer prevention. Research continues to show that diet and exercise have a direct impact on cancer risk.
Precision Nutrition: Precision nutrition tailors dietary advice to an individual’s genetic and health profile. For seniors, this personalized approach can help reduce cancer risks by addressing specific vulnerabilities in their genetic makeup. For example, a 2021 study in The Journal of Nutrition found that a diet high in antioxidants could significantly reduce the risk of developing lung cancer in individuals genetically predisposed to the disease.
Intermittent Fasting: Intermittent fasting has gained popularity for its potential to lower cancer risks. Studies, including research from the National Institute on Aging, suggest that intermittent fasting may help reduce inflammation and promote cellular repair, which can lower cancer risks. For older adults, intermittent fasting, under medical guidance, could provide a simple, effective way to improve overall health and reduce cancer susceptibility.
Exercise: Regular physical activity is one of the most effective ways to prevent cancer. The American Cancer Society reports that regular exercise reduces the risk of breast, colon, and other cancers. Exercise helps maintain a healthy weight, regulates metabolism, and improves immune function—critical factors in preventing cancer. For seniors, activities like walking, swimming, or yoga are gentle on the joints while still offering significant health benefits.
4. Reducing Environmental Risks: Protecting Against Carcinogens
Environmental factors play a significant role in cancer development. Reducing exposure to harmful substances is crucial for prevention.
Pollution and Toxins: Air pollution, chemical exposure, and smoking are all linked to an increased risk of cancer. A 2018 study published in The Lancet found that exposure to air pollution significantly raises the risk of lung cancer. For older adults, reducing exposure to pollutants—such as using air purifiers or avoiding polluted areas—can lower cancer risks.
Wearables for Health Monitoring: Wearable devices that monitor environmental factors like air quality are becoming increasingly popular. These devices track pollution levels and other environmental risks, offering real-time data that can help seniors make informed decisions about their health.
Reducing Radiation Exposure: Excessive radiation exposure from mobile devices and X-rays increases cancer risk. For older adults, minimizing exposure by using protective devices or limiting time spent on electronic devices can significantly reduce the risk of developing cancer.

5. Personalizing Cancer Prevention: The Future of Tailored Healthcare
Personalized medicine is the future of cancer prevention. By tailoring prevention strategies to an individual’s specific genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors, healthcare providers can offer more effective cancer prevention measures.
Genetic Profiling: Genetic profiling allows healthcare providers to identify individuals who are genetically predisposed to certain cancers. This information can be used to create customized prevention strategies that target the individual’s specific risk factors.
AI-Driven Health Assistants: AI-powered health assistants are emerging tools that track health data, detect patterns, and offer personalized advice. These tools can help seniors make informed decisions about their lifestyle and healthcare, reducing cancer risks in the process.
Gene Editing and Stem Cell Therapy: While still experimental, technologies like CRISPR gene editing and stem cell therapy offer the possibility of directly correcting genetic mutations that predispose individuals to cancer. For older adults, these emerging technologies could provide transformative options for cancer prevention.

Conclusion: Embracing the Future of Cancer Prevention
The future of cancer prevention looks promising, especially for older adults who face increased cancer risks. Through advancements in early detection, immune system enhancement, personalized nutrition, and lifestyle changes, seniors can take proactive steps to reduce their cancer risks. With cutting-edge technologies like immunotherapy and gene editing on the horizon, the possibilities for cancer prevention are greater than ever. By adopting these innovative approaches, older adults can take control of their health and work toward a cancer-free future.
